Sivapithecus 1-2
Miocene. Golden age of hominoids
Climate
Continental shifts. Collision between South Asian plate and Southern Asia was producing Himalayan plateau. Miocene considerable warmer than proceeding oligocene.
19 million years ago Arabian plate connected with North East Africa which allowed Migration of animals.
First Fossil in 19 century but complete in 1934. G Edward Lewis. He called it ramapithecus.
Another find was made in Nepal on the bank of Tinau River, Butwal; a western part of the country in 1932. This find was named "Ramapithecus".
Sivapithecus genus. Ape of Shiwaliks.
Time
Miocene ape. Fossils range from 12 and 7 million years ago.
Geographic distribution
Lufang valley China. Turkey 5 skulls. Potwar plateau and Shiwaliks India - teeth and jaw. Nepal Pakistan. lived in mixed Woodland grassland environment.
Classification
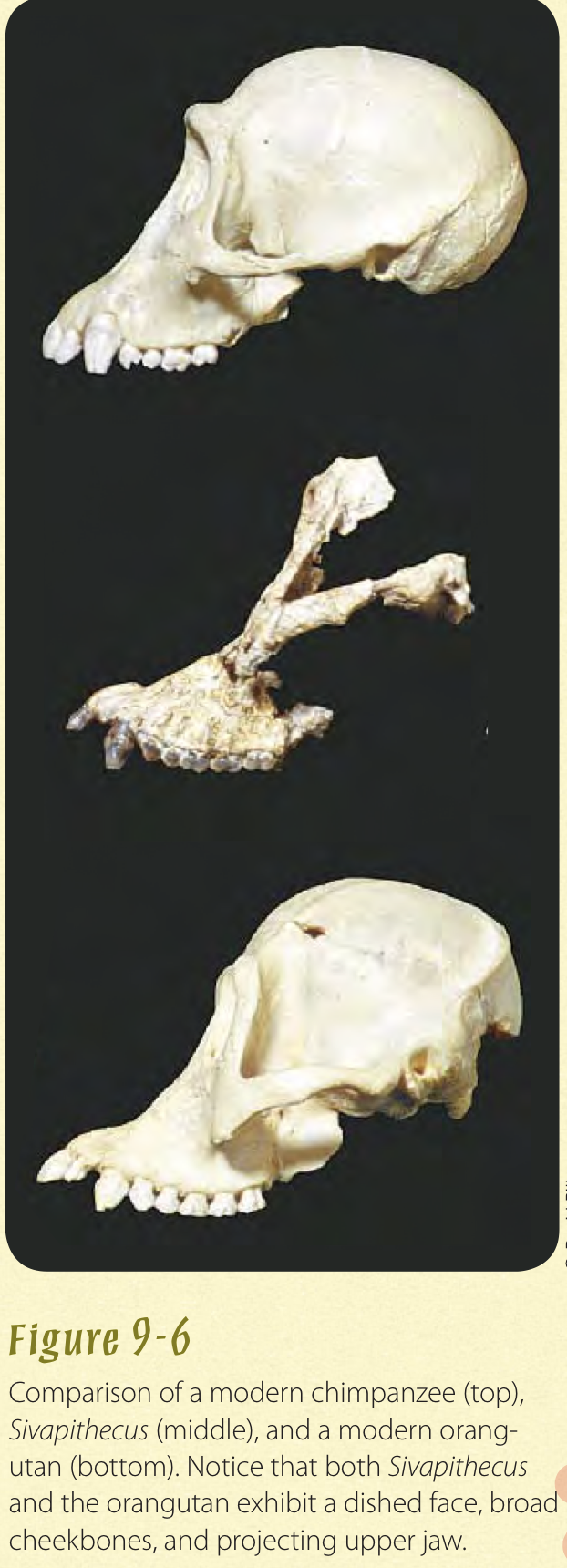
Primate, hominidae, ponginae. Previously believed as human ancestor but now clear that Much closer to modern orangutan.
Species
S. parvada S. punjabicus S. sivalensis
Physical features
- Flat and thickly enameled molars. Smaller canines. Indication of Parabolic dental Arcade. Diastema.
- Modern chimpanzees and Gorilla have thin enamel teeth. Large upper central incisors. Tiny lateral incisors. Large canines.
- Robust jaw bones. concave face, narrow nasal bones, oval eye Orbit from top to bottom.
- Projecting premaxilla
- Diet. Course grasses and seeds point some Scholars argue that fruits were the focus.
- Possibly related to gigantopithecus which had similar teeth to sivapithecus.
- 4.9 ft height. Chimpanzee like feet. Flexible wrists. Large zygomatic bones. Arboreal quadruped. Significant sexual dimorphism.
Debates
- Before 1970 is it was believed that sivapithecus was an ancestor of Hominidae. But in 1979 David Pilbeam and Ibrahim Shah discovered partial sivapithecus Skull. Middle skull in the image.
- Ramapithecus is very similar to sivapithecus but just smaller in size. Possibly a female version of Sivapithecus.
Ramapithecus. Miocene.
Ramapithecus, fossil primate dating from the Middle and Late Miocene epochs (about 16.6 million to 5.3 million years ago). For a time in the 1960s and ’70s, Ramapithecus was thought to be a distinct genus that was the first direct ancestor of modern humans (Homo sapiens) before it became regarded as that of the orangutan ancestor Sivapithecus.
The first Ramapithecus fossils (fragments of an upper jaw and some teeth) were discovered in 1932 in fossil deposits in the Siwālik hills of northern India. No significance was attached to those fossils until 1960, when American anthropologist Elwyn Simons of Yale University began studying them and fit the jaw fragments together. On the basis of his observations of the shape of the jaw and of the morphology of the teeth—which he thought were transitional between those of apes and humans—Simons advanced the theory that Ramapithecus represented the first step in the evolutionary divergence of humans from the common hominoid stock that produced modern apes and humans.
- Simons’s theory supported by David Pilbeam and soon gained wide acceptance among anthropologists.
- The age of the fossils (about 14 million years) fit well with the then-prevailing notion that the ape-human split had occurred at least 15 million years ago.
- American biochemist Allan Wilson and American anthropologist Vincent Sarich,
- who, at the University of California, Berkeley, had been comparing the molecular chemistry of albumins (blood proteins) among various animal species.
- They concluded that the ape-human divergence must have occurred much later than Ramapithecus. (It is now thought that the final split took place some 6 million to 8 million years ago.)
- Wilson and Sarich’s argument was initially dismissed by anthropologists, but biochemical and fossil evidence mounted in favour of it.
- 1976, Pilbeam discovered a complete Ramapithecus jaw, not far from the initial fossil find, that had a distinctive V shape and thus differed markedly from the parabolic shape of the jaws of members of the human lineage.
- He soon repudiated his belief in Ramapithecus as a human ancestor, and the theory was largely abandoned by the early 1980s.
- Ramapithecus fossils subsequently were found to resemble those of the fossil primate genus Sivapithecus, which is now regarded as ancestral to the orangutan; the belief also grew that Ramapithecus probably should be included in the Sivapithecus genus.