Adolescent 2-2
Adolescent
- begins with puberty.
- Sexual maturation. Breast and menstruation in girls. Voice deepening of boys and facial hair in boys.
- secondary sexual features changes to genitals.
- Sexual dimorphism in girls and boys changes in body size.
- During adolescence boys can grow 9 centimetre and girls 7 centimetre but complete their growth later than girls. 21 for biys and 18 for girls.
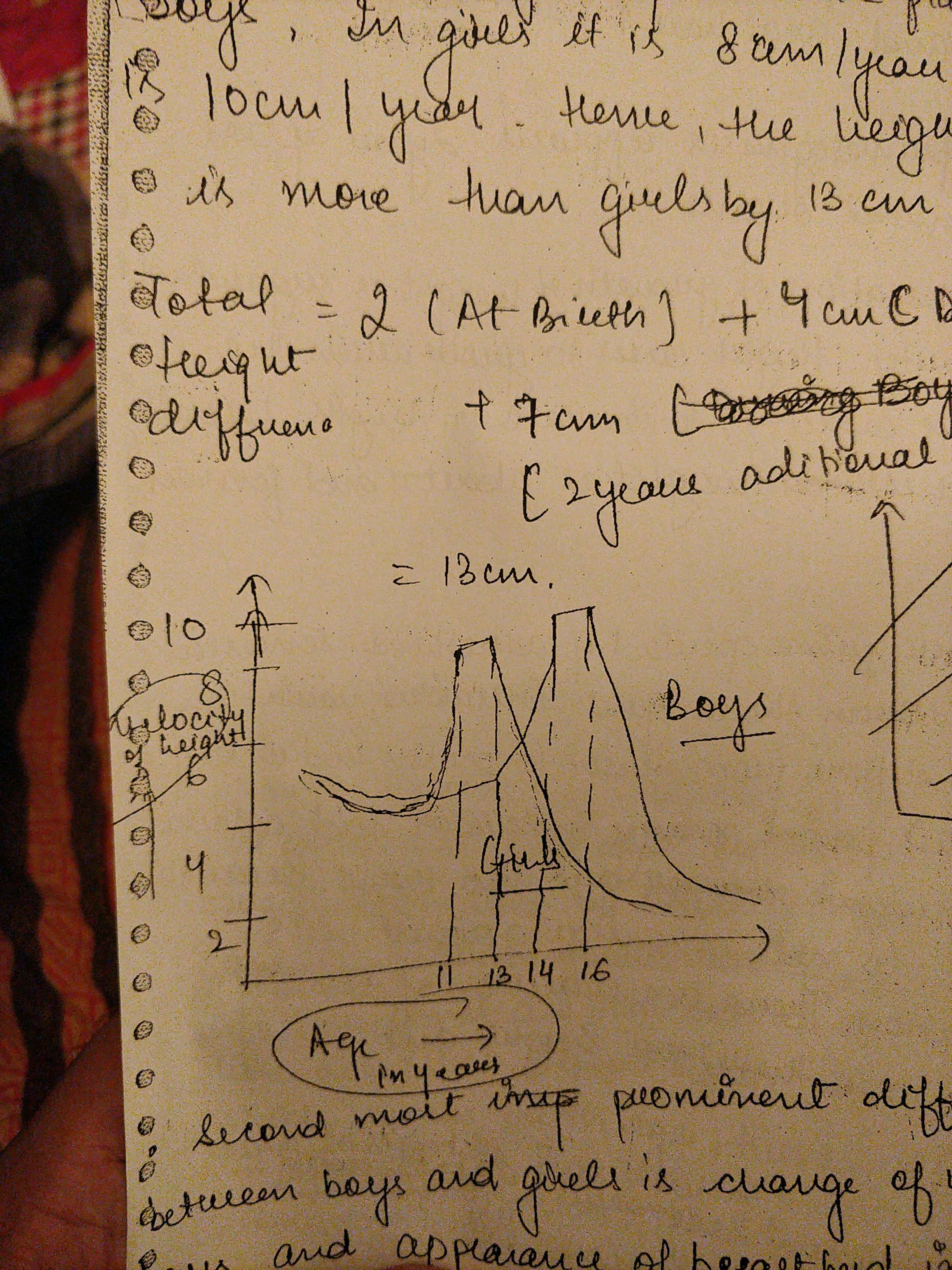
- If there is stress growth may not happen. Quechua Indians of Peru live in higher altitude suffer from cold, over, malnutrition and hypoxia. Growth minimised.
- End of long bones humerus radius and ulna in the arm and femur tibia and fibula in the leg - fuse. epiphyses fused to diaphyses. Height growth ends.
- Influenced by social economic condition, nutrition, genetic disposition, sex hormones.
- DoraCosta and Richard have shown changes in heights of American Europeans between 1710 and 1970. Height increase with living conditions and food. decline in 1830 with urbanization. More diseases and crowded cities. Garbage and polluted water. Then increase as sanitation nutrition and health improved.
- Growthand development in male population is is more sensitive to environment than females. Larsen 2016.
- NUtritionstress can be caught up later by rapid growth.
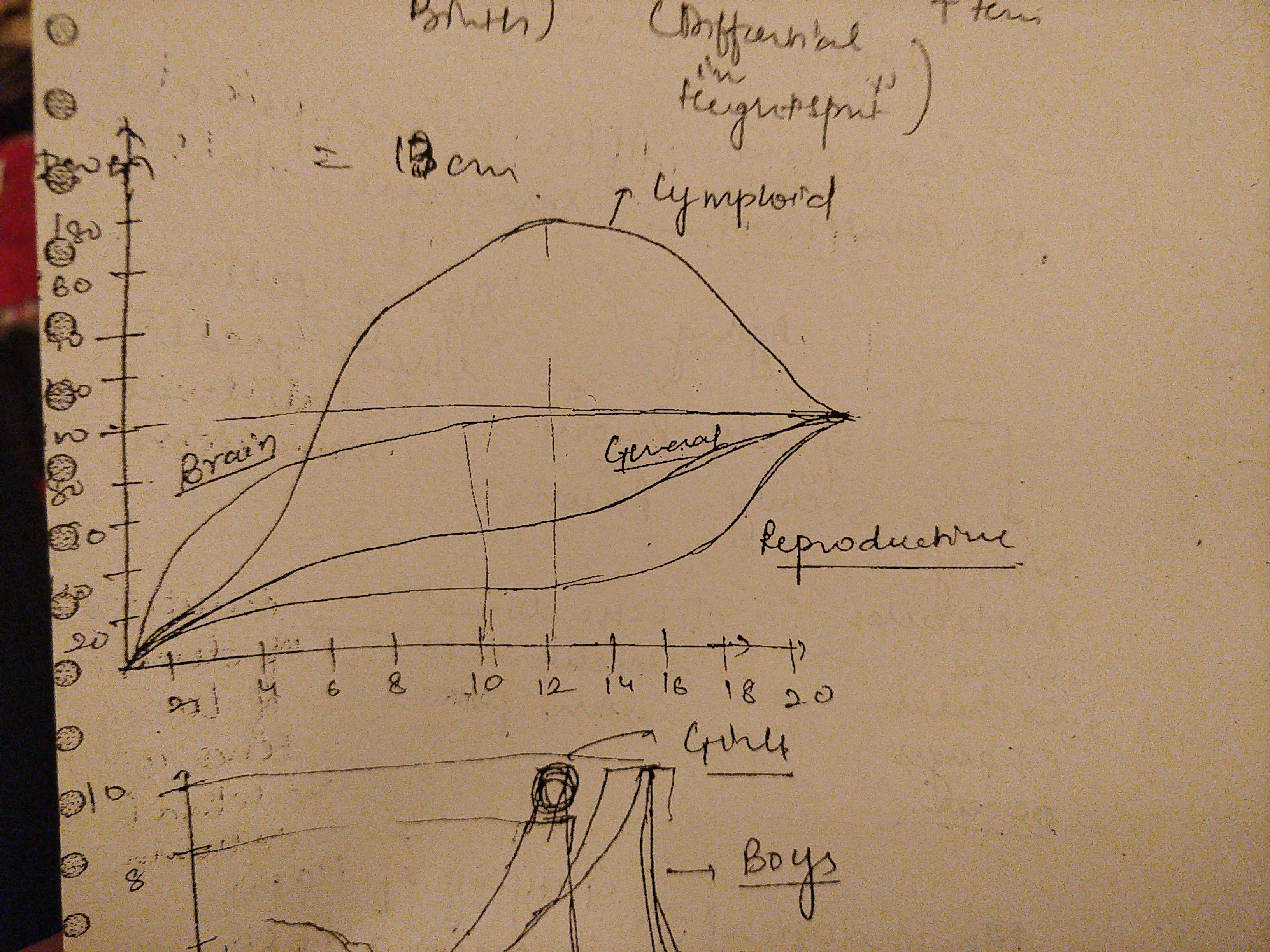
Adult stage
- reproductive period from 20 till 50 for women and senescence Period after childbearing years. Psychological maturation mein take time where as social maturation depends on social life. Cultural differences on what a mature adult is.
- Senescence. Reduction in homeostasis and susceptible to to environmental stress.
- •Women experience menopause around 50 but it varies across populations.
- •Male sperms decline in form and motility by 70.
- •Bone loss osteoporosis. With bones become fragile. It hip knee.
- •Menopause links with bone degradation. Again where is well population genetics and habits like smoking or chronic diseases.
- •Declining function of organs and tissues.