Methods of studying 1-2
Methods of studying growth
- Growth is quantitative change in an organism over time. It may be positive or negative point study usually focus on height, weight, organ growth, bones, muscles etc
- Longitudinal method.
- Repeated measurement of same individual or groups at different times. For example height change with age. This provides a pattern of growth of height in children of a group
- Can be plotted on a graph.
- Provides us insight on factors affecting the treat like height affected by nutrition, war, socio-economic condition, region and so on.
- Distance curve shows overall growth which time.
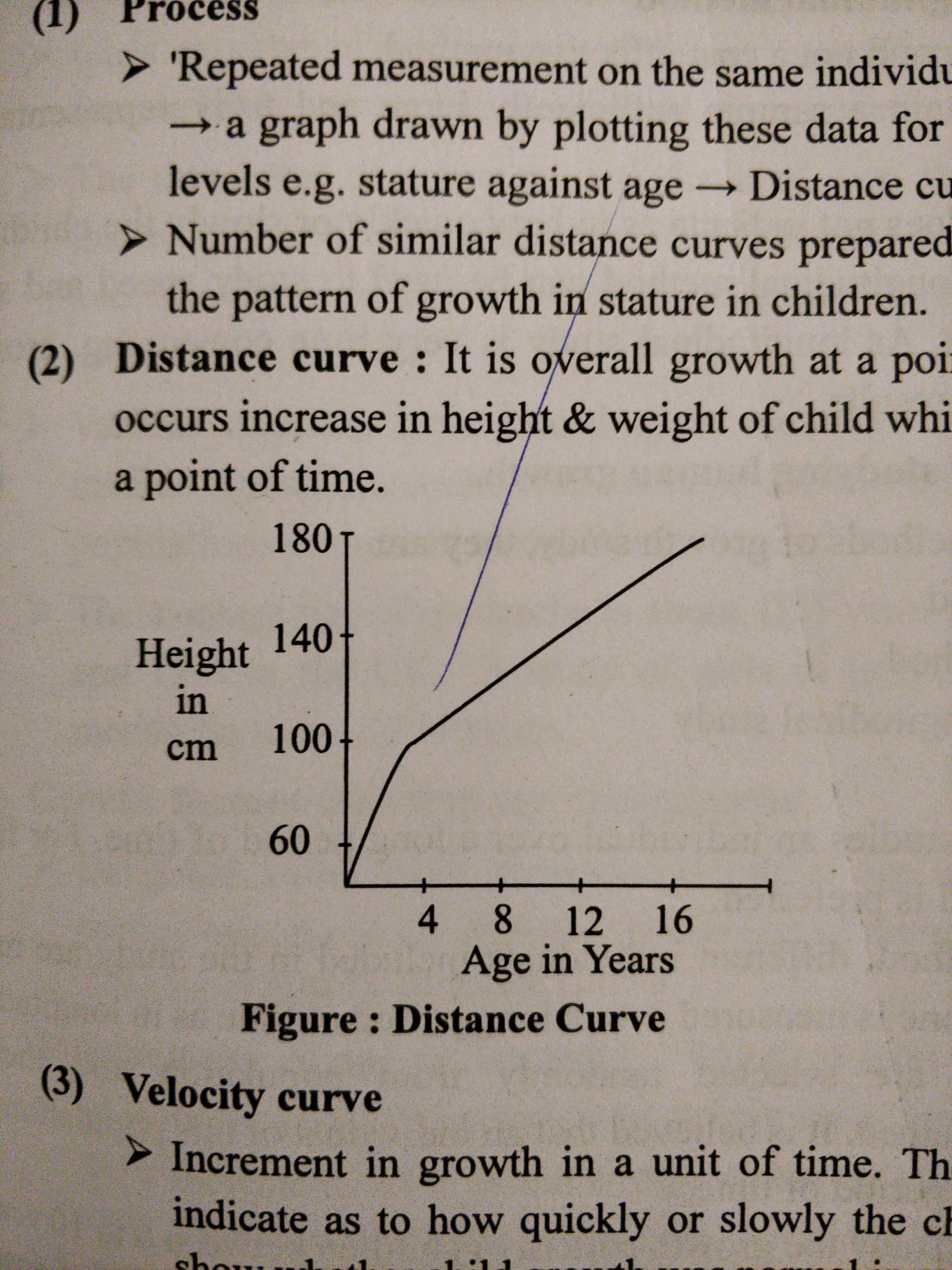
- Velocity curve is rate of growth per unit time. It indicates how quickly growth is taking place.
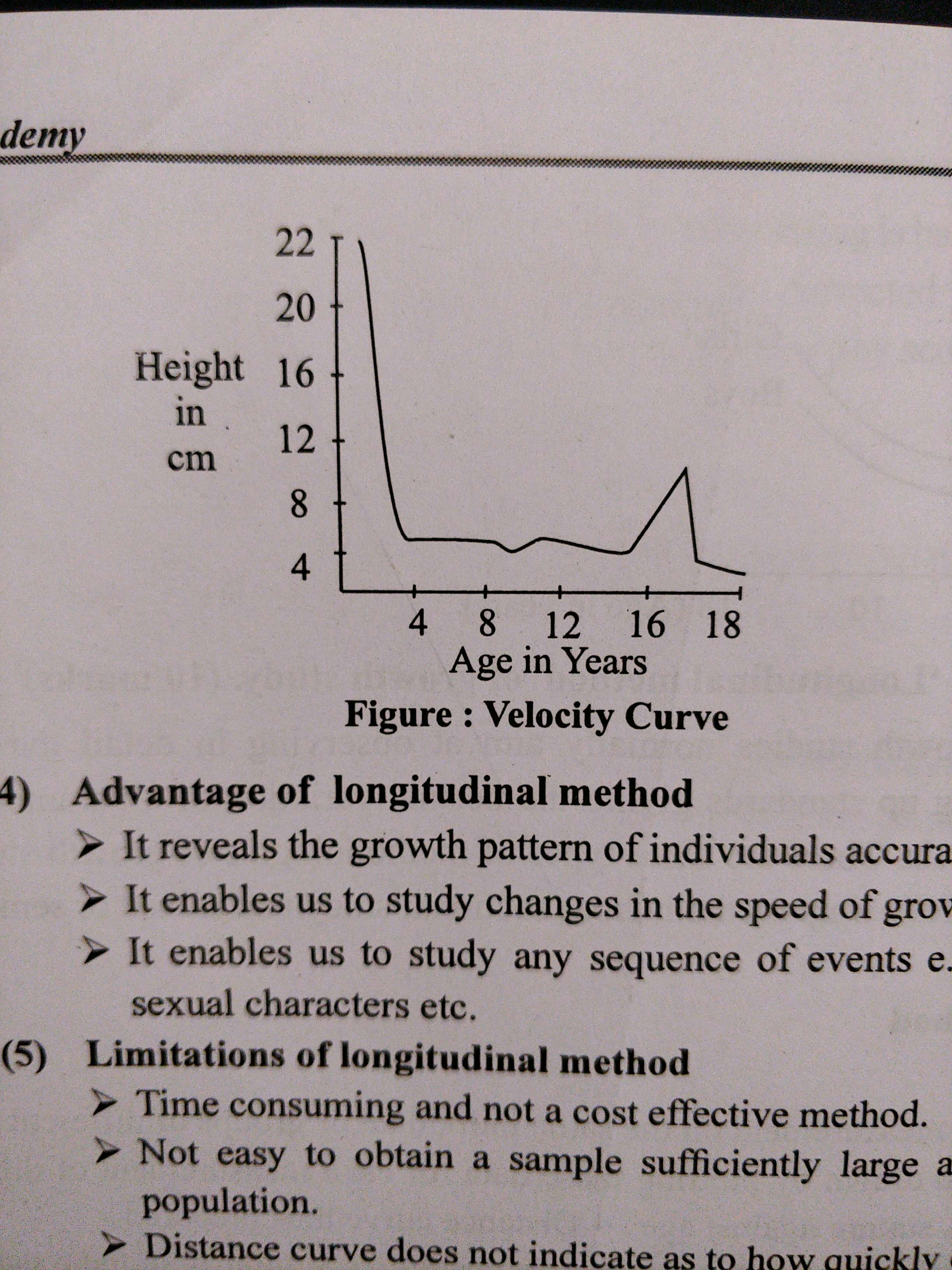
- Advantages.
- accurate growth pattern of individuals.
- Allows us to study speed of growth.
- Interlinked. CanCan study various traits like secondary sexual traits and dentition.
- Accurate study of factors affecting growth
- Limits.
- time consuming and. Time as a confounding variable
- not cost-effective.
- Not easy to obtain large sample and subjects mein stop coming.
- Researcher gets old.
- Baxter 1995 longitudinal study on athletic males swimmers Soccer and tennis players. About 10 years.
Cross sectional method
- Studies different individuals at various stages of life. For example studying children between 6 and 16 so the researcher will take a sample from each age group and compare them.
- Advantage.
- Fast
- cost effective and
- Less burden on researcher.
- Fair estimate on data
- Limitation. not accurate and cannot precisely point towards factors affecting growth specially in an individual. persons as confounding variable.
- Luna 1983. Cross sectional study of effect of puberty on insulin.
Therefore semi longitudinal mixed method is used.